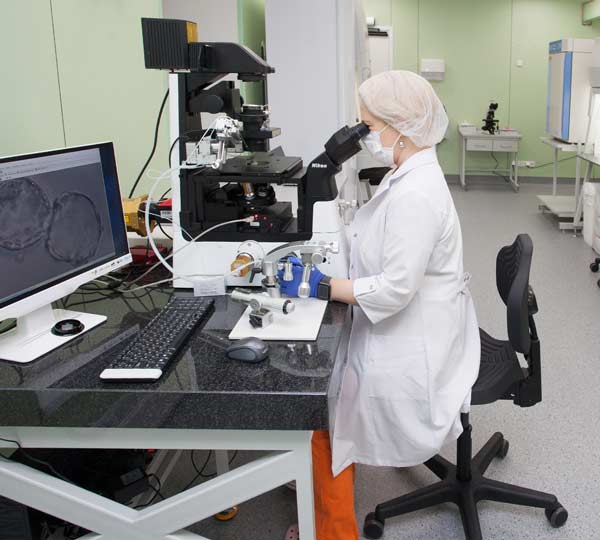
A | | |
1) common term for all the mutation types - deletions, translocations, inversions, duplications; 2) genome mutations - aneuploidies, trisomies | | |
The absence of the menstruation in a woman of reproductive age. Primary amenorrhoea – the initial absence of the menstruation; secondary amenorrhoea – the absence of the menstruation at least for the last six month. | | |
A male sex hormones. | | |
A change in the number of chromosomes, where abnormal numbers of specific chromosomes or chromosome sets exist within the nucleus. | | |
Occurring, existing, or performed before birth, during pregnancy. | | |
Placing sperm into the vagina or uterus. Nowadays, intrauterine insemination is only used. | | |
The opening of the embryo’s covering using, for example, a laser aimed at facilitating implantation of the embryo. | | |
Reduced sperm motility. | | |
A non-sex chromosome. In humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. | | |
The medical condition of a man not having any spermatozoa in his semen. Azoospermia has two forms: abstructive azoospermia and non-obstructive azoospermia. | | |
| ||
1) General name of any mutation – deletions, translocations, inversions, duplications. 2) Genomic mutations (aneuploidies, trisomies, etc.). | | |
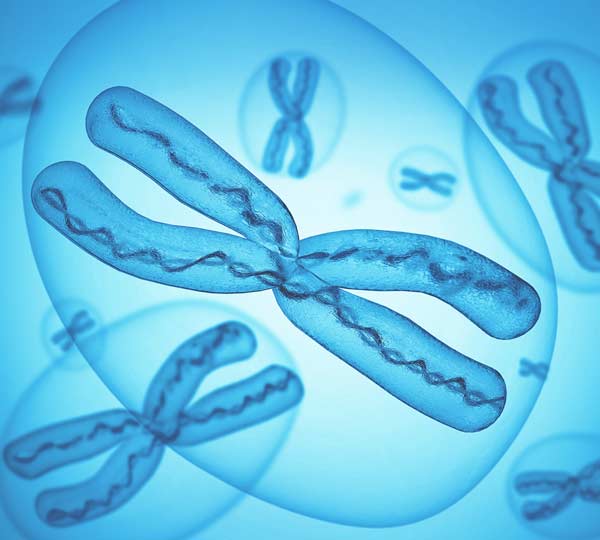
A threadlike structure in the cell nucleus consisting of DNA and special proteins and providing hereditary materials. Chromosomes contain all or most of the genes of the organism. | | |
From Greek: kryo = cooled, frozen. The cryopreservation is used to preserve the supernumerary embryos, which can then be used for further attempts. Also, spermatozoa can be cryopreserved. | | |
| ||
1) A type of chromosomal aberration in which part of a chromosome is missing. 2) A type of genetic aberration in which a DNA molecule loses its part. | | |
Induced by medicines decrease in endogenous output of hormones. | | |
| ||
A pathological pregnancy, in which implantation has taken place in any tissue other than the uterine wall. | | |
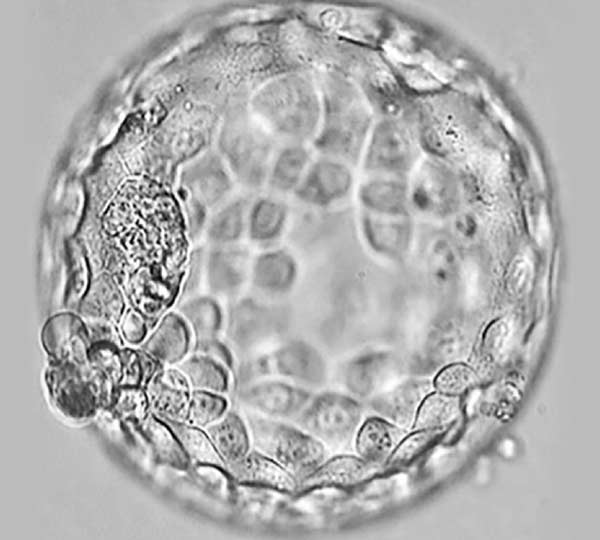
The developing human individual from the time of merging of male and female genetic material in the fertilized egg. Since the 13the week of pregnancy the embryo becomes a fetus. | | |
Placing a dividing fertilized oocyte (embryo) into the uterus with the intent to establish pregnancy. | | |
A frequent cause of the infertility. A common medical condition where the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium) is found outside the uterus causing scar formation. | | |
The abundantly supplied with blood membrane lining the inner surface of the uterus that gets renewed periodically. Embryo implants in endometrium. | | |
From Latin: östrus = readiness to coupling, gen = to cause. Estrogens – female sex hormones produced in the ovaries and controlling the growth of the endometrium. | | |
| ||
Two very fine funnel-shaped tubes that guide spermatozoa to the oocyte and the fertilized oocyte – to the uterus. | | |
The quality or state of being fertile. | | |
The interaction of gametes. | | |
A vesicle in the ovary that contains a developing egg surrounded by a covering of cells. Follicles mature in the ovaries. | | |
Piercing a follicle with a very fine needle to obtain an oocyte. | | |
(follicle stimulating hormone) A hormone produced by the hypophysis and stimulating the growth of immature follicles to maturation. | | |
| ||
Sex cells (ovum and spermatozoon). | | |
A functional unit of inheritance controlling the transmission and expression of one or more traits. A trait can be controlled by several genes. | | |
A term composed of two roots of English and Greek origin: gonos = reproduction, trop = influence on, releasing = setting free. A hormone responsible for release of FSH and LH. | | |
A medicine initially causing increase in FSH and LH secretion, then however it induces a profound hypogonodal effect achieved through downregulation. | | |
| ||
Carriers of information between different organs in the body. | | |
From Latin: chorion = fetal integument, gonad = gonads, trop = to affect. A hormone produced in pregnancy which is medically used to cause ovulation. hCG is extracted from the urine of pregnant females or it is synthesized using biochemical technologies. | | |
From Latin: Menopausa = climax, gonad = sex gland hMG is produced from a sterile preparation of placental glucoprotein urine of post-menopausal women. hMG is used to stimulate ovaries. | | |
The main endocrine gland, controlling functioning of other endocrine glands (gonads, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, etc.); sits in the small, bony cavity at the base of the brain. | | |
| ||
Embedding of the embryo into the endometrium. | | |
From Latin: in vitro = in a test glass, fertilisation = fertilization. IVF means fertilization outside the body. | | |
If a regular sexual life doesn’t result in conceiving a child within a year, physicians call this infertility. However, this state isn’t unchangeable or unrecoverable. | | |
The term is composed of words with roots of Latin origin: intra =in, inside, cytoplasma = content of a cell, spermium = spermatozoon. An in vitro fertilization procedure in which a single sperm is injected directly into an oocyte using a finer microneedle. | | |
| ||
The chromosomal characteristics of a cell; the complete set of chromosomes of a diploid cell; (normal human female karyotype -46, XX; male karyotype - 46, XY); the set of chromosomes specific to this particular organism. | | |
| ||
The time when yellow bodies (corpus luteum) produce progesterone. The lutein phase requires to be supported by administration of exogenous progesterone if there is deficiency in endogenous progesterone. | | |
A hormone that triggers the onset of ovulation. | | |
| ||
A relatively permanent change in hereditary material (DNA, gene, chromosome, genome). | | |
A benign tumor consisting of muscle tissue and normally located in the uterus. Myomas may cause infertility or habitual miscarriage. | | |
| ||
A condition in which spermatogenesis is blocked and no sperm cells are produced . | | |