Synchronization of egg donor's and a recipient's menstrual cycles.
To start egg donation program both egg donor and egg recipient have to be in the beginning of their menstrual cycles. To make this possible, birth control tablets (combined oral contraception tablets) are prescribed to the egg recipient and egg donor. The tablets are taken according to the doctor's plan and finished at the same day by both patients. After cessation of tablets menstruation comes in the egg recipient and the egg donor, so both of them can start their treatment.
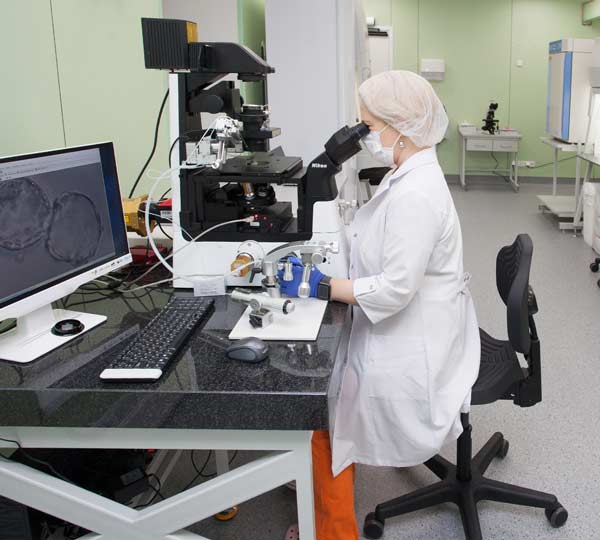
Treatment of the egg donor
The treatment of the egg donor takes about 2 weeks.
Once the egg donor's period begins, an ultrasound examination is performed to make sure the ovaries are inactive and the uterine lining is thin.
In the beginning of menstrual cycle Follicle Stimulating Hormone (Gonal-F, Puregon) is administered to stimulate the growth of ovarian follicles. The hormone is injected subcutaneously once a day. The injection is painless and most women learn to inject themselves. The injection treatment usually takes 9–12 days, and 2 or 3 ultrasound examinations will be performed during the course of the treatment to monitor the growth of follicles in ovaries and the effect of the hormone dosage. After the first ultrasound another medication is added (Cetrotide, Orgalutran). This medication suppresses the egg donor's own hormonal activity and prevents the premature release of egg cells (premature ovulation).
Once follicles have grown sufficiently, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Pregnyl, Ovitrelle) is injected to release the egg cells into the follicular fluid and to cause the final maturation of the eggs. Approximately 36 hours after injection, the eggs are retrieved with a needle inserted through the vaginal wall under the guidance of ultrasound. Full anesthesia will be given intravenously during the procedure. The procedure is fairly quick, and many describe the sensation after the procedure as similar to ordinary menstrual pain. After egg retrieval, the donor must rest for a while to allow the effect of the anaesthetics to wear off. The medication affects reaction speed, so driving is not advised on the day of the procedure. The next period will begin about ten days after the retrieval of the egg cells.
Treatment of the recipient
Once the period begins, an ultrasound examination is performed on the recipient to check that the ovaries have no cysts and the uterine lining is thin. After this, the recipient takes estrogen medication orally to prepare the uterine lining for implantation (Progynova, Progynon, Estrafem). Sometimes medication starts already in the end of the previous cycle, to downregulate own hormones (downregulation) and is continued by estrogens after menstruation start. As the treatment progresses, the recipient will also start using progesterone vaginally several days before embryo transfer (Lugesteron, Crinone, Utrogestan). Ultrasound examinations are performed to monitor the growth of the uterine lining. The examinations can be conducted either at O.L.G.A. Fertility Clinic or by the recipient's gynecologist in home country.
The semen sample of the recipient's husband is needed for the fertilization. Before delivering the sperm sample the husband must be tested for HIV and hepatitis (HIV-Ab, HBs-Ag and HCV-Ab). The tests can be done at a local laboratory. The sperm may be fresh or frozen. Sperm cryopreservation (freezing) may take place during the first visit of the couple to the clinic.
The cells (egg and sperm) are cultivated and cleavage is monitored for 3-5 days, after which a maximum of two high-quality embryos will be transferred into the recipient's uterus. Embryos are transferred through the cervical canal using a soft plastic catheter. The procedure of embryo transfer is usually quick and painless. If there are several high-quality embryos, they can be cryopreserved for later use.
After embryo transfer, estrogen and progesterone therapy continues. Pregnancy test will be taken two weeks after the embryo transfer. If the test is positive, hormone medication will continue until the 12th week of pregnancy. Two weeks from the pregnancy test ultrasound examination will be performed to confirm the pregnancy. If the test is negative, the hormone medication can be discontinued.
As with all pregnancies, assisted pregnancies involve a small risk of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, foetal development defects, and later complications during pregnancy and delivery.
Related pages in other lnguages: English Egg donation Deutsch Eizellspende Netherlands Eiceldonatie Dansk Ægdonation