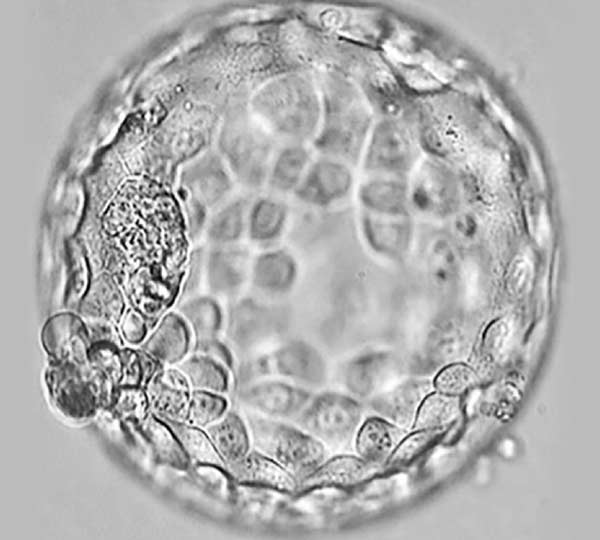
While in 1970, 90% of the parents were under 30 years old when they had their first child, nowadays a third of the parents are above 30 years old. Fertility in women at ages above 30 and especially above 35 decreases considerably. Main causes of female infertility are described below.
Impairment of ocyte (eg) maturation.
The female infertility is often attributed to impairment of oocyte maturation. In most cases the problem is of hormonal nature. Hormonal disorders in women are much more often than men. Disbalance of hormones may result in impairment of oocyte maturation, ovulation and/or corpus luteum ("yellow body") formation. The following endocrine glands produce hormones, that are importent for foolicular growth, oocyte maturationa and yellow body formation – hypophysis, thyroid gland, adrenal glands. If the only cause of infertility is an endocrine disfunction, then hormonal treatment and stimulation of oocyte maturation shall be provided. If several infertility causes are present, treatment methods are selected individually.
Hormonal imbalance may hinder oocyte maturation
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Female infertility is often due to multiple small cysts, fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries, i.e. so called polycystic ovaries. Moreover, it is usually accompanied by elevated androgen level (male hormones). The PCOS infertility is usually connected with impairment of oocyte maturation. The stimulation of oocyte maturation using FSH is quite efficient for treatment of infertility due to PCOS.
Tubal infertility
The fallopian tubes are required for spermatozoa to get to the oocyte and for the fertilized oocyte to wander into the uterine cavity. The fallopian tubes being stuck together, the egg transport is damaged or blocked. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes can be caused by inflammation, previous tubal pregnancy, surgeries or endometriosis. There are several methods of the fallopian tubes patency evaluation. If the fallopian tubes are obstructed, the IVF.may be the method of choice.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the mucus layer of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside its conventional place. The cause of endometriosis is unknown. The endometrial lesions can be located on the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, urinary bladder, bowel, etc. In case of endometrial lesions are localized in the fallopian tubes, the tubes can not function due to the scars. However, the fallopian tubes can still be "open" for fluid. The endometrial lesions microenvironment makes impossible to conceive naturally. Thus, in case of endometriosis IVF may be required.
Disorders of the uterus or uterine cervix.
Scars (surgeries) or immune disorders of the uterine cervix may lead to infertility. Artificial insemination can usually solve this problem.
Uterine myoma is also a common cause of infertility or miscarriage. The necessity of surgical correction is determined by the ultrasound examination.
Ovary, fallopian tubes or uterine malformations.
The malformations reproductive system (usually congenital) that are rare condition, cause infertility.
Immune system disorders.
The disorder of immune responseare very rare and can cause female infertility. The female immune system recognizes the oocytes or spermatozoa as foreign cells and destroys them.
Genetic causes
The most common genetic causes of female infertility are quantitative and structural chromosome aberrations, and a fragile X syndrome. The genetic causes less often cause infertility in women than in men. In 25-50% the primary amenorrhea (no menstruation at the age of 16 or above) is caused by chromosome anomalies including the Terner syndrome (karyotype – 45,X), which occurs in 1 in 2500 – 3500 thous. of newborn girls.
In case of the secondary amenorrhea (the woman has menstruated at one time, but has not had a period for six months or more), the karyotype anomalies occur in 10-15% of patients.
In families with a complicated obstetric history (recurrent miscarriage, especially at early term, mortinatality, children born with multiple congenital abnormalities – chromosome anomalies occur in 5-15% of cases.
The cytogenetic analysis (karyotyping) for female infertility is recommended in the following cases:
- Primary amenorrhea
- Secondary amenorrhea
- Slow sexual development syndrome
- Recurrent miscarriage
Up to 5% of women with premature menopause are fragile X syndrome carriers. This syndrome is the most common cause of the congenital impairment of mental development and is more typical for boys. The genetic basis of fragile X syndrome is an expansion of a definite region of the female X chromosome in women carriers.
The molecular genetic studies for fragile X syndrome are recommended for the patientys with:
- premature menopause
- primary amenorrhea