New details about the identity, role, and function of human genes, their modifications resulting in hereditary disorders are constantly emerging. Genetic counseling and examination help to reveal these disorders, and select an efficient method. This process usually starts with a genetic counseling.
Genetic counseling if offered in our clinic to infertility patients or couples with a high risk of hereditary disease in an offspring. In the last decade more genetic causes of male and female infertility became known. Different types of genetic examination, such as chromosome screening (karyotype) for both partners, molecular genetic diagnostics, prenatal diagnostics, preimplantation genetic diagnosis are available in our clinic.
What is a genetic counseling?
- Identifying of genetic causesof infertility.
- Evaluation of risk of hereditary disease and/or infertility in offspring.
- Prevention of hereditary disease and/or reproductive disorder in offspring.
- Consulting on many issues associated with the disease, including medical, psychological and social aspects.
We support the patients' initiative to make their own decision. We provide them with all required information. Everyone shall keep in mind that the decision is individual and shall not depend on any global issues. The doctor's contribution is to discuss all the issues, provide information, and recommend the patient and, if required, his/her relatives to undergo additional testing. The major diagnostics procedures are prenatal diagnostics, preimplantation genetic diagnosis, karyotype, molecular genetic diagnostics. The patients get accurate and honest information on the advantages and the risks of diagnostic procedures. All these procedures are available in our clinic.
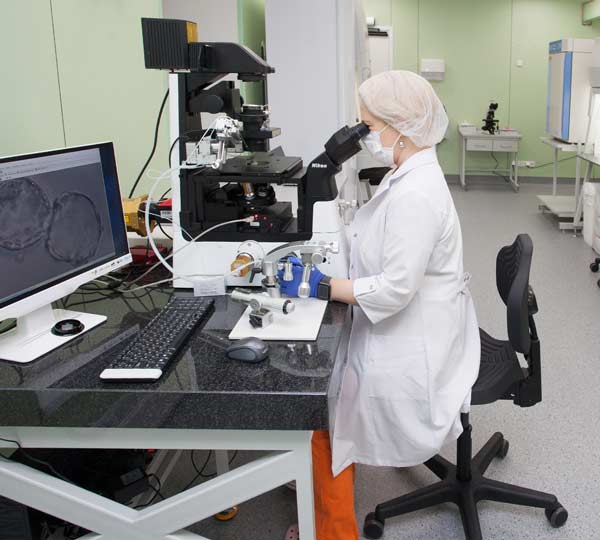
Cytogenetic method (Karyotyping).
Any living organism has a specific set of chromosomes called a karyotype. A karyotype consists of 46 chromosomes – 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Women have two X chromosomes (karyotype: 46, XX), men have one X chromosome, and one Y chromosome (karyotype: 46, XY). Each chromosome carries genes responsible for inheritance. A karyotype is examined using cytogenetic and molecular genetic methods.
Karyotyping is a cytogenetic method which helps to reveal numerical and structural chromosomal aberrations. These aberrations can result in infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, hereditary disease in an offspring.
Molecular genetic diagnostics
Hereditary diseases are often due to alterations in a DNA molecule. If a large DNA area (chromosomal disk) is affected, that can be identified using microscope. In this case cytogenetic methods (karyotype) may be sufficient to identify the diagnosis. If a small DNA area (single gene) is mutated, karyotype making is not sufficient and additional molecular genetic methods shall be applied. These methods help identifying even tiny changes in the gene's DNA sequence.